In this guide, we’ll explore how Data Cloud transforms businesses’ insights and actions through harmonization, unification, and activation. Learn how the platform functions, the advantages it offers, and the crucial steps involved in turning disparate data into actionable, real-time insights.
What is Data Cloud?
Data Cloud is a platform that acts as a central hub for all customer data from various sources. It’s equipped with connectors that can gather information from different sources—like Salesforce apps, mobile and web platforms, connected devices, and even legacy systems—ensuring that all this data is updated in real-time.
This consolidated data becomes the single source of truth for the company. Essentially, Data Cloud helps businesses get a clear, real-time view of their customers’ data from all different areas.
How Does Data Cloud Work?
Step 1: Data Sources
Data Cloud gathers data from different places.
Step 2: Connect and Ingest
It uses various connectors to bring all this data together, including Salesforce Cloud, Amazon S3, Google Cloud, web and mobile sources, APIs via MuleSoft, and custom API connections. This makes the process faster and integrates external data from multiple data lakes.
Step 3: Harmonize (Map)
The collected data is then organized into a common structure based on Salesforce Customer 360, ensuring that everything is uniformly identified, from individuals to transactions.
Step 4: Unify
Data Cloud merges customer identities across common data points (like email addresses or names), providing a unified view of each customer.
Step 5: Analyze and Predict
The unified data can be used within Data Cloud for insights like Customer Lifetime Value. It can also be connected to external AI or BI tools for predictions, recommendations, and data exploration.
Step 6: Act
As a result, companies can act based on this unified data—updating pages, triggering flows, making decisions, and publishing unified customer segments for advertising or marketing. In short, Data Cloud streamlines data from the entire Salesforce Platform to save time and personalize customer experiences.
Data Cloud Advantages
- A unified view across the company for engagement, analytics, machine learning, and actions.
- Empowerment of all users, from developers to business analysts, with the strength of big data.
- Consolidated, reliable source of information by uniting billions of profiles and digital engagements.
- Real-time engagements across various channels and touchpoints
What Does Data Cloud Magic Consist Of?
Data Ingest
To start working with big data in Data Cloud, we need to select the Data Source and Data Source Object.
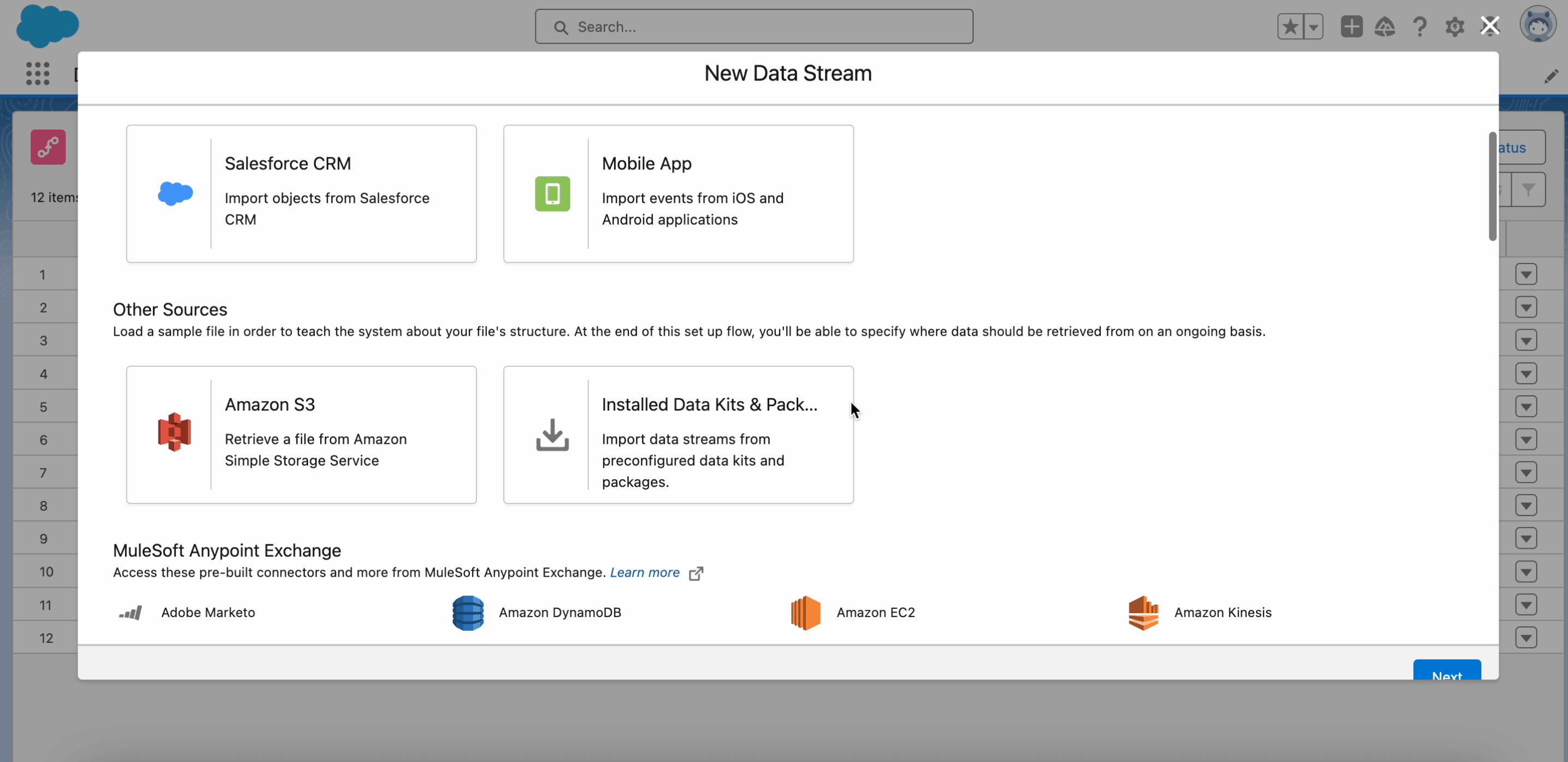
Examples of Data Source Object:
- In Marketing Cloud, it can take the form of a data extension.
- In Salesforce CRM, it might be a Contact or Case object.
- In B2C Commerce, it can be a Sales Order Customer Entity or a Sales Order Entity.
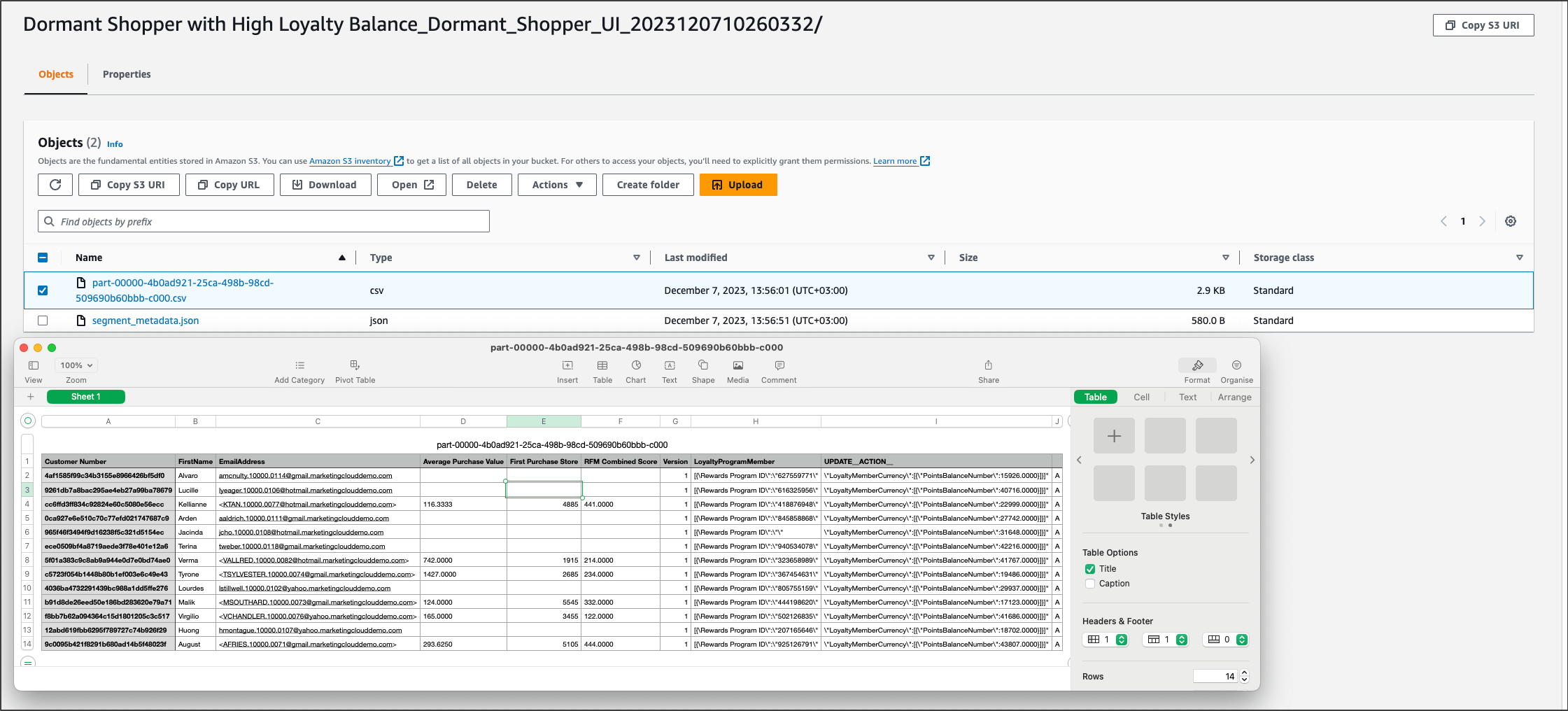
- In AWS S3 (or another storage), it may be represented as a .csv file.
Then, we define Data Stream Properties. This section focuses on two key fields when defining the data stream properties:
- Source Name: This field pinpoints the source system (e.g. AWS S3 Bucket details).
- Category: This field dictates the purpose of the data (Profile, Engagement, Other).
As a final part, we confirm the Data Source Object Schema.
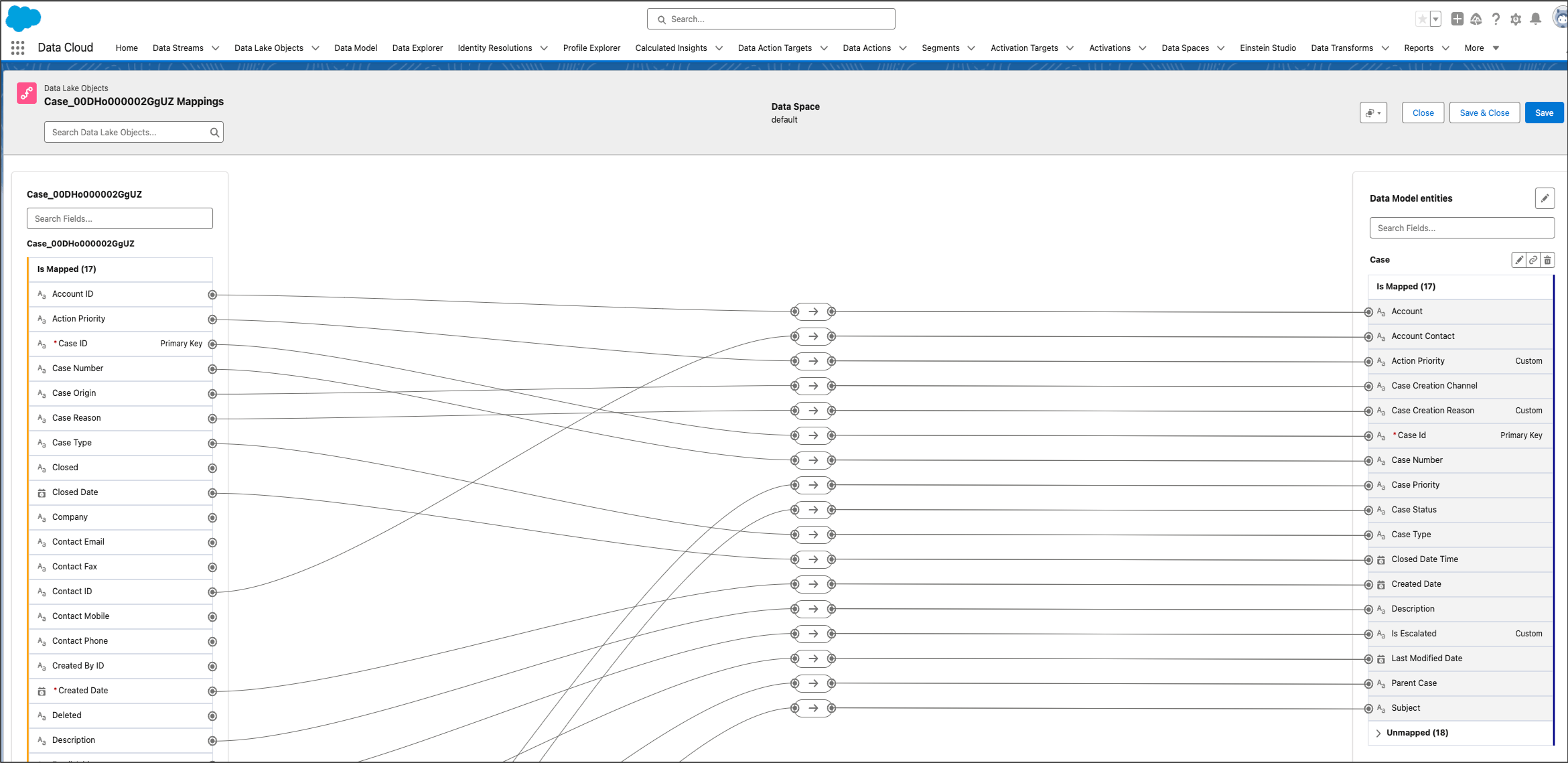
Data Mapping
Once the data from all data streams is ingested, it gets written to data lake objects. Following the creation of your data streams, it’s essential to link your data lake objects to data model objects.
The best practice for mapping is to ensure all objects are tied back directly or indirectly to an entity that will be used in segmentation.
When mapping data, it’s also important to keep in mind:
- The data category.
- Extending the Data Model (using standard, customizing standard, creating a new one—via copy from existing/from file/new).
- Required mappings.
Specific data mappings are essential for the Data Cloud to maximize its impact across harmonization, unification, and activation processes.
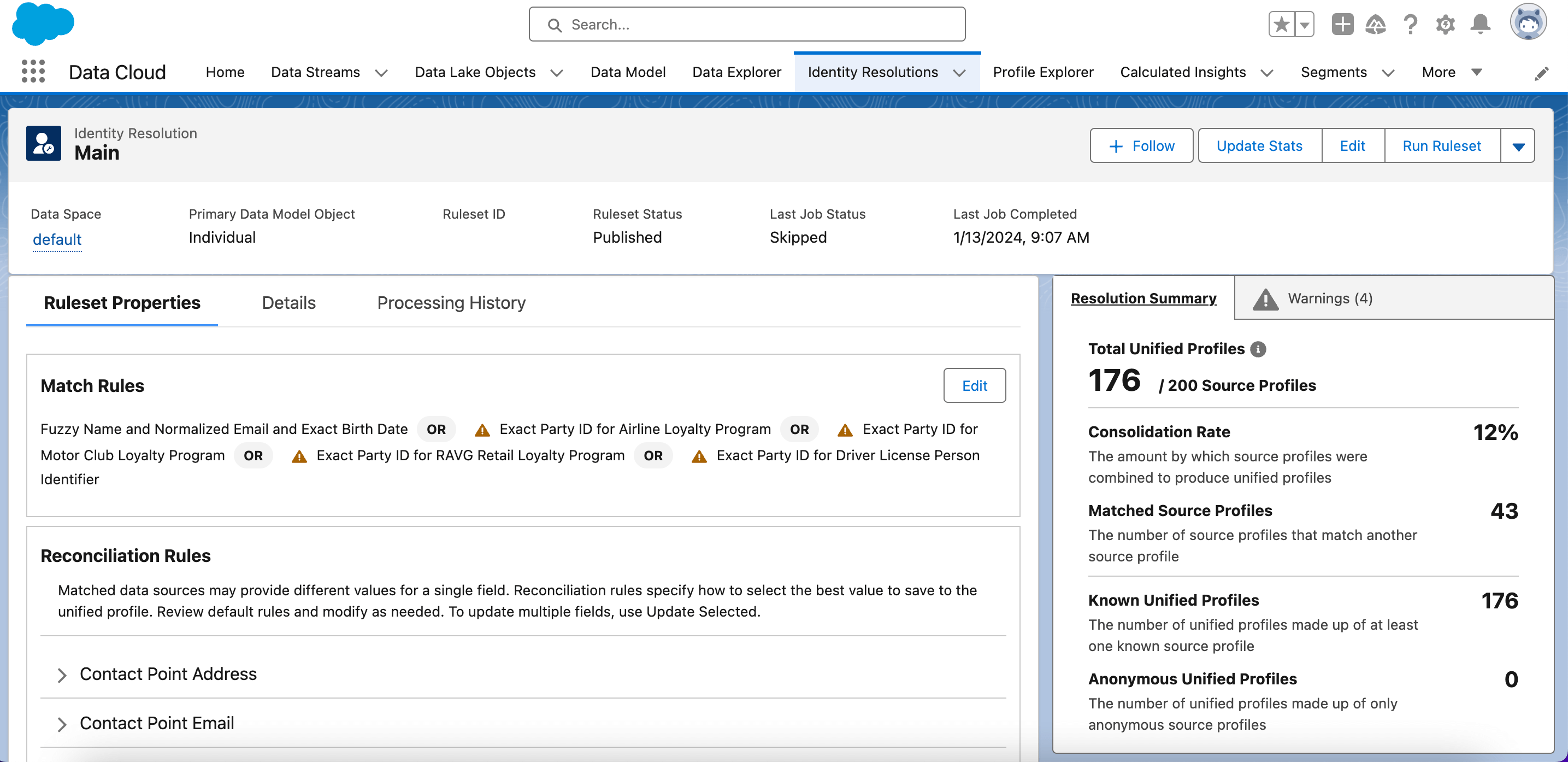
Identity Resolution
Identity Resolution helps to consolidate data from various sources into a comprehensive customer view, known as a unified profile.
Identity resolution is performed by creating a Ruleset, adding Match Rules, and configuring Reconciliation Rules. Results will include the number of total unified profiles created.
Segments
The core of Salesforce Data Cloud is its segmentation engine, empowering business users to:
- Search through all the data in the system.
- Form detailed customer segments.
- Gain insights into the data composition.
Segmentation is used to break down data into helpful segments to understand, target, and analyze customers.
Real use-case scenario: Identify customers with a significant balance of loyalty points but low spending activity (e.g., no purchases in the last quarter). The goal is to then send these customers a promotion encouraging them to utilize their loyalty points for purchases.
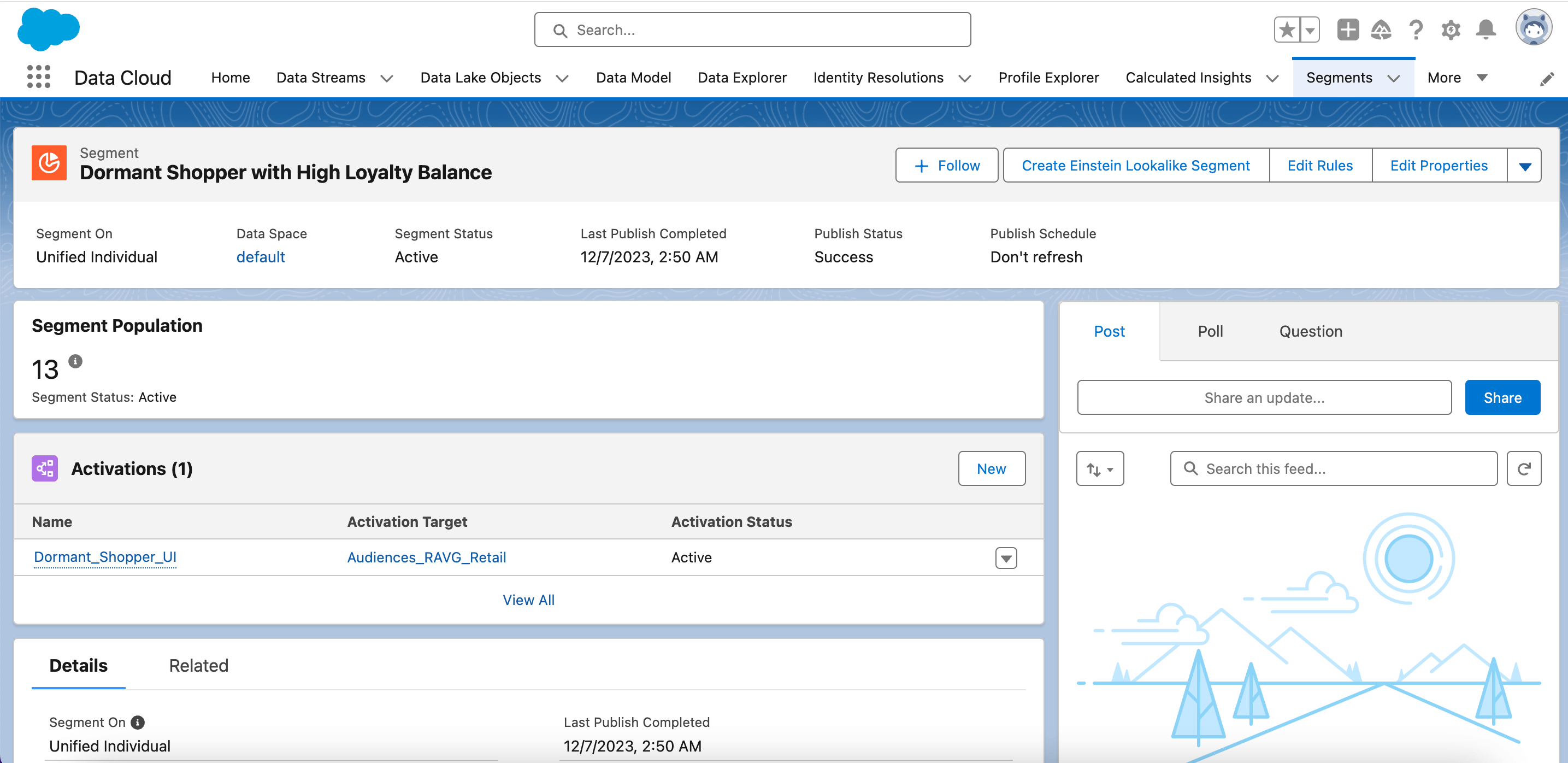
Segment Activation
In Data Cloud, you can craft audience segments for tailored marketing campaigns within Journey Builder. These segments can also be used across various advertising partners, such as Facebook (Meta) and Google.
Moreover, within Data Cloud, you can act on the data to create enriched experiences through:
- Segment Activation, allowing you to materialize and publish your segment to activation platforms.
- Data Actions, which enable you to act on streaming data and insights to trigger actions based on specific conditions, thereby empowering downstream systems to drive an action or orchestration.